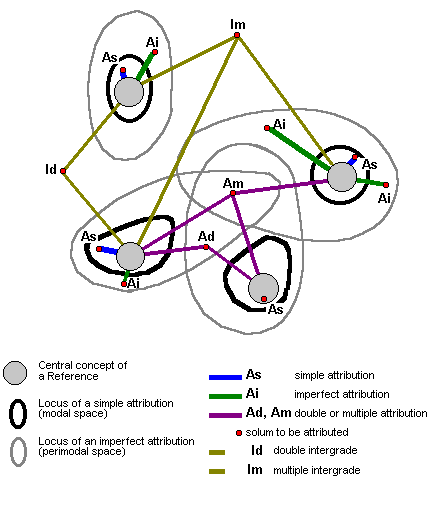

However, each Reference is defined by several characteristics, qualitative (ordered or not) and quantitative. It is possible to apply the notions of modal and perimodal ranges in a multi-dimensional space with N dimensions. If the solum studied is located inside the modal space of a Reference, that is a simple attribution. If the solum is located inside the perimodal space of a Reference, that is an imperfect attribution. If the solum is outside the perimodal space of a Reference, it is not possible to make an attribution and the solum is considered an intergrade.
There is little chance that a solum under study corresponds exactly to the definitions of the Référentiel Pédologique. A simple attribution accepts therefore some small differences from the central definition of a particular Reference. In other words, a simple attribution is within the modal space of a single Reference.
Here differences become important and are greater than those allowed within the modal space of a Reference, although they are within its perimodal space. In this case, it must be clearly indicated that some properties do not correspond exactly to the definition of the closest Reference. For example : a LUVISOL TYPIQUE which has partly lost its E horizons by erosion ; an ORGANOSOL CALCIQUE containing insufficient carbon (6.5 % instead of the 8 % required) to qualify fully.
Often, solums which may be linked to two References are encountered, and the pedologist does not wish to emphasize one more than the other. For example, particular soils can obviously be assigned to LUVISOLS because the illuviation process is clearly seen and is shown by a distinct structural and textural differentiation ; such soils however show also waterlogging at shallow depth which cannot be ignored. In such cases the solum lies within the perimodal space of two References : a double attribution is therefore necessary to provide complete information and to give the best possible picture of the reality. Such a solum is called a LUVISOL-RÉDOXISOL. Similarly, a triple attribution could be possible.
The term of intergrade is applied to sola with properties outside the perimodal spaces of the nearest References. In the R.P. system, a solum may be located half-way between two References (a double intergrade), but it could equally be linked to three or even four References (a multiple intergrade). For example, among the black soils of Limagne there are sola which may be assigned to the CHERNOSOLS, the RÉDUCTISOLS and the VERTISOLS. It is useful to be able to indicate this threefold relationship.
 Home Page Home Page
|
Last modification by dbz@denis-baize.fr :
|